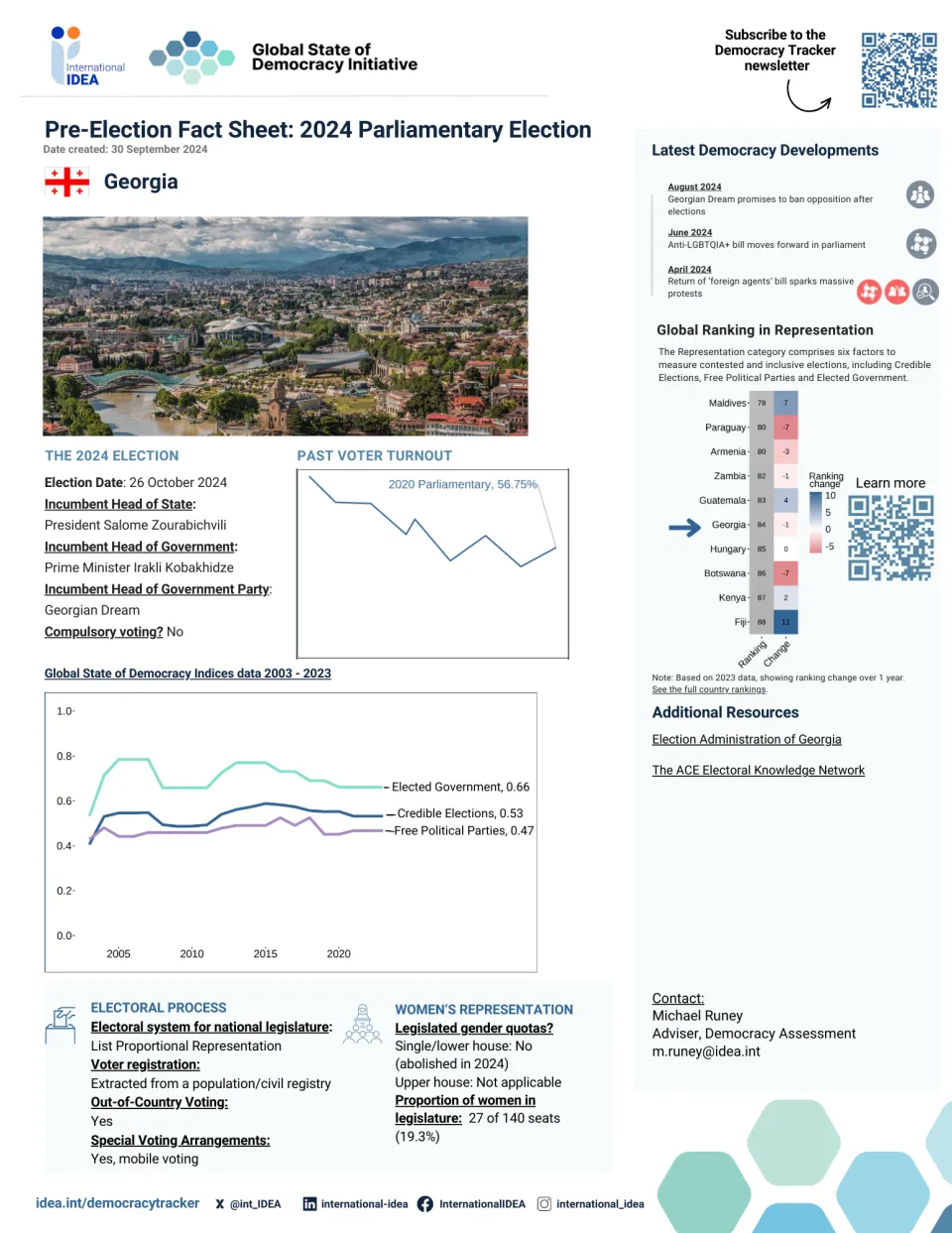
Georgia
Georgia exhibits mid-range performance across all Global State of Democracy (GSoD) categories of democracy. It ranks in the top 25 per cent globally in Absence of Corruption, and over the past five years, it has experienced significant declines in six factors, including Credible Elections, Civil Society, and Civil Liberties Some of these concerns are due to heavy-handed repression of anti-government protesters and civil society as well as hostile environment for media. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Georgia endured years of political instability and a severe economic collapse, but is now an upper-middle-income country and mid-performing democracy. Historically, much of Georgian public policy was oriented towards obtaining membership in NATO and the European Union, but in recent years the ruling Georgian Dream has backtracked on both goals. Economically, Georgia is dependent on remittances from the 23 per cent of the labor force that works outside the country.
Georgia is overwhelmingly composed of ethnic Georgians (86 per cent or the population), but has sizable Azerbaijani, Armenian, Abkhaz, Ossetian and other smaller minorities. Ethnic minorities’ grievances in the early years of independence strengthened separatist Abkhaz and Ossetian movements, leading to the Georgian Civil War (1991-1993). Russia intervened on behalf of Abkhaz and Ossetian separatists, and the war ended after the displacement of roughly 300,000 people -- primarily ethnic Georgians -- from the self-declared and largely unrecognized Republics of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Then in 2008, Russia baited an incautious Georgian President Mikheil Saakashvili into providing an excuse to launch a full-scale war, which resulted in Russia establishing de facto control over both separatist republics and displacing an additional 135,000 Georgians and Ossetians. As of 2024, about 299,000 Georgians (eight per cent of the population), are registered as internally displaced people, and hold an uncertain place in Georgian society.
Georgian politics have been dominated by the ruling Georgian Dream party, which has controlled the parliament and nearly every municipal government continuously since defeating Saakashvili’s United National Movement in 2012. Since then, Bidzina Ivanishvili, who is the head of the UNM and Georgia’s richest man, has been Georgia’s de facto ruler, despite having only intermittently held office. Although the parties have historically largely agreed ideologically, identity-based polarization has become intense in recent years, and Georgian Dream’s formal ‘pause’ of European Union accession in 2024 was met with widespread protests. Simultaneously, the government has moved to severely restricted media, opposition political party and civil society freedom through direct prosecutions and by cutting off sources of nongovernmental funding.
Georgia performs in the mid-range on Gender Equality and elected its first woman president in 2018. However, women’s and LGBTQIA+ rights have suffered under Georgian Dream’s restrictions of rights and liberties; parliament repealed a 2020 gender quota in 2024 and LGBTQIA+ people are officially portrayed as an unwanted Western import.
Having abandoned the broadly popular goal of EU membership, Georgia’s trajectory in the next five years will be determined by how far Georgian Dream takes its authoritarian turn and reorientation towards Russia. Moves to single out critical journalists for prosecution and shutter media outlets entirely means it Freedom of Expression and the Media may be at risk, and efforts to politicize the civil service may indicate further declines in Predictable Enforcement.
Updated: May 2025
https://www.idea.int/democracytracker/
November 2025
Parliament approves end of out-of-country voting (OCV)
Georgia’s Parliament passed in the first reading on 25 November amendments to the country’s Electoral Code to end out-of-country voting (OCV). An estimated 1.5 million Georgian citizens live outside of the country, compared to 3.7 million in Georgia itself. Over 95,000 Georgians abroad registered and 34,574 voted in the most recent general elections at 60 voting stations in 42 countries. Media reported that long lines prevented many voters from participating. Civil society experts say the government is motivated by its unpopularity among the diaspora. Georgian Dream had received 53.9 per cent of the vote overall but 13.5 per cent abroad. Parliament Speaker Shalva Papuashvili said the move was needed because voters in the United States and European Union were ‘vulnerable to external interference’ and the results showed ‘how open and blatant foreign informational and political pressure on voters can be.’ The bill will now need to be passed in a second reading and signed by the President to become law.
Sources: Civil.ge, Caucasian Knot, Civil.ge
Anti-Corruption Bureau to be abolished
The Georgian Government has announced the Anti-Corruption Bureau will be abolished by 2 March 2026. All its functions are to be transferred to the State Audit Office. While the Bureau was created at the urging of the European Commission as part of conditions for Georgia’s European Union candidacy, it had in recent months been a key part of the crackdown on civil society by subjecting critical civil society organizations and media to punitive audits. Leading Georgian Dream officials have said the Bureau’s existence was ‘dictated from the outside’, meaning the European Union, and centralizing anti-corruption responsibilities under the State Audit Office would be more efficient.
October 2025
Georgian Dream seeks to ban political opposition
The Georgian Parliament adopted legislation that grants the Constitutional Court the authority to prohibit individuals associated with banned political parties from forming or joining political parties, standing as candidates in elections or holding any public office. Legislation passed in May 2025 already allows the Court to ban any political party it sees as aiming to ‘overthrow or change Georgia’s constitutional order by force, undermine the country’s independence, violate its territorial integrity, engage in war or violence propaganda, incite national, regional, religious, or social strife’. It can also ban parties that it sees as identical to a party already subject to such a ban. Officials from the ruling Georgian Dream Party have said the purpose of the legislation is to empower it to ban the country’s three major opposition parties, which it accuses, without evidence, of seeking to overthrow the state, and that it intends to file a lawsuit to begin the process in the immediate future.
Sources: First Channel, Civil Georgia, OC Media, Parliament of Georgia
August 2025
NGO crackdown continues with bank account freezes
The Georgian government froze seven leading civil society organizations’ (CSO) bank accounts on 27 August, as part of anti-corruption and tax inspections it has undertaken on nearly every high-profile CSO in the country since the country’s Foreign Agent Registration Act came into effect in June. The freezes are part of a case alleging the CSOs are engaged in ‘sabotage’ by allegedly purchasing protective materials for anti-government protesters and paying arrested protesters’ fines and legal fees. In statements, the affected CSOs denied the charges and said the protective materials in question were purchased for their own staff, as their mandate as human rights monitors required them to monitor protests. In March 2025, the Prosecutor General’s Office froze the bank accounts of other CSOs that had financially supported protesters, but has not yet provided any evidence to support the current charges.
Sources: Eurasianet, OC Media, International IDEA
May 2025
Georgian Dream steps up pressure on opposition parties
The ruling Georgian Dream party escalated its efforts to ban and sideline opposition politics parties in May. Three opposition leaders were sentenced to pre-trial detention and Parliament (boycotted by the opposition) passed a law simplifying the process and expanding the criteria for banning political parties. Zurab Japaridze, Irakli Okruashvili and Nika Gvaramia were arrested for declining to appear before a parliamentary committee tasked with investigating alleged crimes of the former United National Movement (UNM) government (2004-2012). The committee’s stated goal is to find grounds to ban UNM and all other opposition parties. Many opposition figures have refused the committee’s summons, arguing that the committee’s aims are unconstitutional and that because the 2024 parliamentary elections lacked credibility, the current Parliament is illegitimate. If convicted of failing to comply with the summons, all three face up to one year in prison and a three-year ban from holding public office.
Update: Zurab Japaridze and two other opposition politicians were sentenced to eight months in prison on 23 June for failing to comply with the parliamentary committee’s summons. Japaridze and Mamuka Khazaradze and Badri Japaridze (no relation) of Lelo Party were also banned from holding public office for two years. Five other opposition politicians are still awaiting sentencing.
Sources: OC Media (1), OC Media (2), OC Media (3), Parliament of Georgia, International IDEA, Civil.ge
See all event reports for this country
Global ranking per category of democratic performance in 2024
Basic Information
Human Rights Treaties
Performance by category over the last 6 months
Blogs
Election factsheets
Global State of Democracy Indices
Hover over the trend lines to see the exact data points across the years
Factors of Democratic Performance Over Time
Use the slider below to see how democratic performance has changed over time